.
What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in an assisted reproduction treatment and how to prevent it? This side effect, which appears on rare occasions, starts to be noticed a few days after the administration of hCG. hCG is given approximately 36 hours before the ovarian puncture to trigger ovulation.
To minimise your chances of ovarian hyperstimulation, at Juana Crespo, we always take all possible precautions and carry out regular checks on your progress. This way, we monitor your response to the medication given. As with each phase of the treatment, the stimulation protocol is customised according to your age, BMI, etc. And only with continuous monitoring will we ensure that your hormone levels are adequate.
If you are undergoing assisted reproduction treatment or are planning to start one soon, it is important that you are informed about all aspects. From the Juana Crespo Team we answer 10 questions about ovarian hyperstimulation in IVF.
1- What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome is an exaggerated response to hormones. These hormones are administered in certain assisted reproduction treatments in order to stimulate the formation and maturation of eggs.
OHSS is a very unlikely complication, but it may occur in IVF. This is because more hormones are administered in IVF than in other treatments such as artificial insemination.
On the other hand, in the case of egg donation or embryo adoption, the patient will not undergo the stimulation phase during her treatment. She is therefore exempt from any risk derived from this stimulation.
2- What does ovarian hyperstimulation consist of?
Hormonal medication in IVF allows your ovaries to be stimulated, but what happens when this response is greater than expected? Most often, your ovaries increase in size and fill with fluid. This is what is known as Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome. The most significant consequence of this is the release of this fluid into the abdominal cavity.
3- Why does it occur?
The excessive reaction to ovarian stimulation in IVF usually appears in the luteal phase of the cycle, specifically after the injection of hCG.
Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone, hCG, is usually the last injection of assisted reproduction treatment. Its administration triggers ovulation so that the ovarian puncture can be performed 36 hours later. It is also the hormone that the body generates during pregnancy.
hCG, together with the administration of gonadotropins during the previous 10-12 days, which stimulate the growth of the ovarian follicles, are the triggering factors of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome.
This hormonal treatment also increases the permeability of the blood vessels. This can cause fluid to be released from the bloodstream and fill the ovaries or abdomen with fluid.
However, don’t panic.
OHSS is rare and, if it does occur, the discomfort is usually mild to moderate.
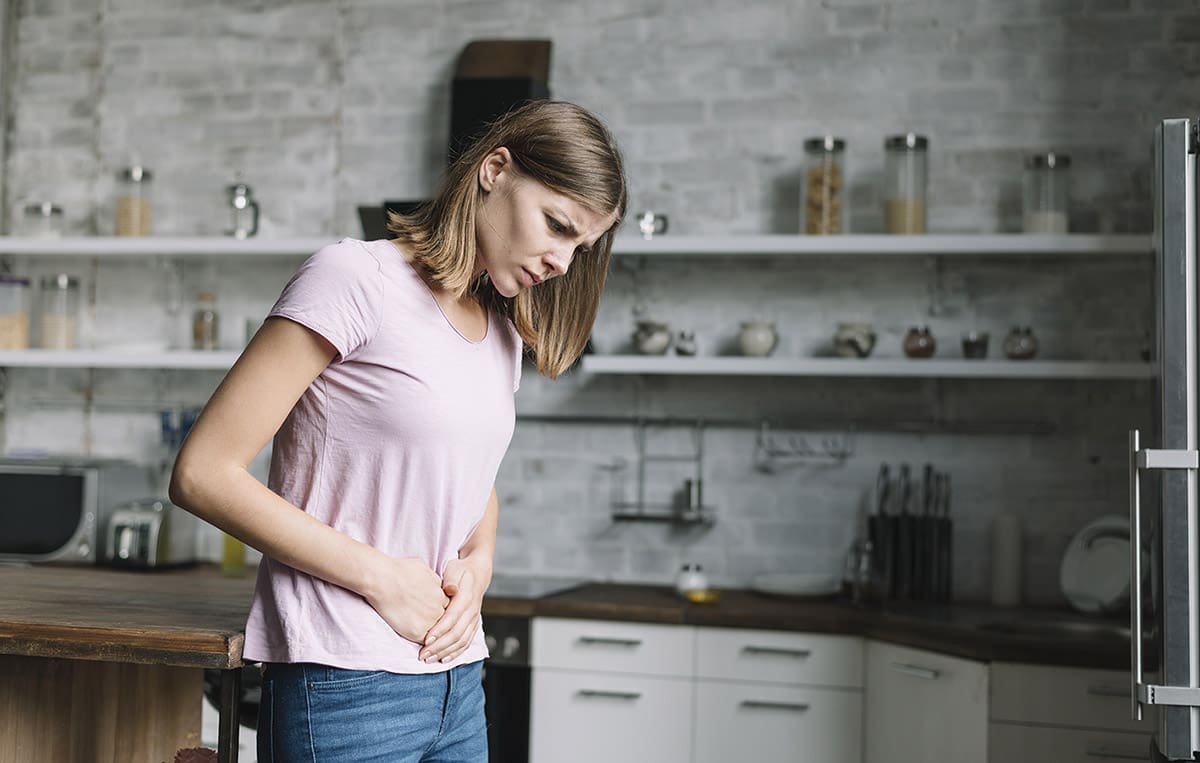
4- What are the symptoms of ovarian hyperstimulation?
As we mentioned above, most women who suffer from Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome have mild or moderate symptoms. If this is your case, you may experience some of the following effects:
- Swelling and mild pain in the abdomen.
- Tiredness and heaviness
- Weight gain
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
5- What should I do if I have any of these symptoms?
If this happens, you should contact the clinic. Your doctor will then be able to quickly provide you with guidelines to follow.
It is very important that you listen to your body and be aware of your discomfort. At Equipo Juana Crespo, we have a Medical Care unit and a 24-hour emergency number. All of this, with the sole purpose of helping our patients, especially if you notice that something is not going well or if you have any questions or concerns.
6- Which women are more likely to develop ovarian hyperstimulation?
Although OHSS is uncommon, it does not only affect women with a certain profile. However, there are a series of risk factors that favour its appearance:
- Age. Younger women, under the age of 30, have more follicles and are better responders, which makes them more susceptible to an exaggerated response.
- Low body mass index (BMI), i.e. thin women.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), as women with PCOS usually have more developing follicles that are stimulated by the hormones given.
- Pregnancy. If you become pregnant during treatment, the presence of the hCG hormone could worsen the development of OHSS. It is therefore essential that you report the above symptoms to us as soon as possible.
- Previous episode of OHSS. If you’ve alreadyhad this syndrome in the past, you are more likely to suffer from it again.
8- What is the treatment?
The treatment will depend on each case, especially on the severity of the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome you suffer from.
If your case is mild or moderate, the treatment will be aimed at reducing discomfort. In general, it is best to follow the following guidelines:
-
- Take painkillers to alleviate the pain. The most common in these cases is to take paracetamol, but it is very important that you do not self-medicate. Your specialist should be the one to determine your personalised treatment.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially drinks rich in mineral salts (isotonic drinks).
- A diet rich in protein is recommended.
- Rest with your legs raised to avoid thrombotic processes.
- Do not drink alcohol or caffeine.
- Avoid exercise. In cases such as OHSS, excessive physical activity is not recommended due to the risk of ovarian torsion.
- Avoid sexual intercourse, as this could lead to multiple pregnancies and aggravate OHSS.
9- Ovarian hyperstimulation, when does it disappear?
The duration of OHSS is usually short, as it generally disappears when menstruation stops. This would be 10-14 days after the ovarian puncture.
However, as we have already mentioned, if you have become pregnant during this cycle, the symptoms may be prolonged and aggravated. In this case, your gynaecologist will closely monitor your progress until your body manages to release all the fluid and your hormone levels stabilise.
10- How can ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome be prevented?
It is true that this syndrome does not develop until days after the hCG injection. This is when you can be diagnosed with OHS with certainty.
However, in the assisted reproduction clinics we carry out different tests during the treatment to assess the possible risks. At Equipo Juana Crespo we leave nothing to chance and we study any signs that may give your gynaecologist clues about the risks of suffering from this syndrome.
- Signs and signals that warn of OHSS
- Elevated oestradiol. If we see elevated oestradiol levels or a rapid increase in a short period of time in blood tests, we can suspect possible OHSS.
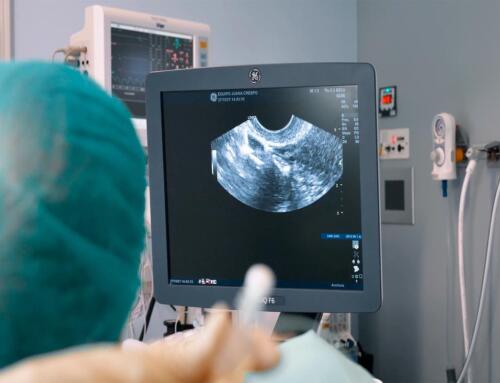
- High number of stimulated follicles. If in the ultrasound we see many follicles in development or that these are distributed around the ovary like a necklace, we will watch out for any indication of OHSS.
- Previous episode of OHSS. If you have suffered from OHSS before, your gynaecologist will change the hormone dose to prevent a new episode.
- Strategies to avoid Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
At Equipo Juana Crespo we develop fully customized assisted reproduction treatments (age, BMI, medical history, response to medication, etc.). However, we can also adjust the different phases of the treatment depending on the response we obtain. Therefore, if you are at high risk of developing OHSS due to your characteristics, we will be able to adjust the different phases of the treatment depending on your response.
- Reducing gonadotropin doses
We have already seen that gonadotropic hormones are partly responsible for OHSS. To avoid their effects, we carry out a personalised and very controlled stimulation protocol. - Replacing hCG with other drugs
There are other drugs that are also very effective in provoking ovulation and preventing OHSS. However, it must be taken into account that they can also reduce the rate of implantation and pregnancy. - Canceling the cycle
In the event that we see follicular development too rapid or your blood estradiol levels are excessively high, it may be advisable to cancel the cycle. - Advance follicular puncture
With follicular puncture we manage to reduce the ovarian volume and reduce the number of active granulosa cells. To do this, it is advisable to remove all the follicles (mature and immature) from your ovaries. - Postpone the transfer and freeze the embryos.
If we have done the puncture and we suspect that you may develop OHSS, we can vitrify all the embryos to perform the transfer in a later cycle. This does not prevent the onset of OHSS, but it does prevent the worsening that could occur in the event of gestation.
We know that strategies such as these (cancelling the cycle or postponing the transfer) delay your dream of becoming a mother. However, these are some of the options that we will take into consideration to prevent or avoid worsening ovarian hyperstimulation.
At Juana Crespo we not only want your pregnancy, but we also have the responsibility to ensure that your pregnancy evolves and that you can have a healthy baby at home. For this reason, our team does exhaustive monitoring with constant controls and tests that help us to achieve our common goal: your motherhood.
If you want to avoid OHSS or you have already suffered from it in a previous cycle in another clinic and you do not want the discomfort to happen again, we can help you at Juana Crespo. We have professionals specialised in highly complex cases. We are very attentive to your treatment and evolution, and we have emergency telephone assistance 365 days a year.
If in addition to these 10 questions about ovarian hyperstimulation in IVF, you would like to ask more questions, you can book your first consultation now on 961 042 557 or through our email: info@juanacrespo.es
.