Ovarian stimulation is to regulate or modify the woman’s menstrual cycle and provoke a multiple ovulation. Its objective is to obtain quality eggs and increase the chances of becoming pregnant.
The growth of several follicles in the ovary is achieved thanks to the administration of a personalized hormonal treatment depending on the ovarian reserve, the Body Mass Index (BMI), the age of each woman and her medical history.
Ovarian stimulation medication can also be modified depending on the patient’s response or the type of treatment. For example, the ovarian stimulation medications and their dosage are not the same for In Vitro Fertilization as they are for egg donation.
In order to understand this procedure, we will first tell you how the ovary works.
How does the ovary work?
The ovaries are the female reproductive glands, whose main functions are:
- To secrete estrogen and progesterone, the hormones responsible for female sexual characteristics (such as breast development) and for regulating the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
- Harboring and releasing the egg.
At the beginning of each menstrual cycle, follicles, which are small fluid-filled structures containing the egg, grow inside the ovary. An egg can potentially develop in each of these follicles.
As the menstrual cycle progresses and depending on hormone levels, so-called “follicular recruitment” occurs, and only one of the follicles is able to respond to hormones and develop. The rest will be lost.
Around day 14 of the cycle, there is an increase in the hormone (LH) and its peak causes ovulation: the follicle in the ovary ruptures, the egg is released and the fallopian tube is responsible for capturing it so that it can be fertilized.
During menopause, the ovaries stop producing hormones and releasing eggs, which means the end of a woman’s fertile period.
On what day of the cycle does ovarian stimulation begin and what are its phases?
The phases of ovarian stimulation are:
- Initial basal ultrasound. This involves performing an ultrasound scan in the first 3 days of the period, or while taking contraceptives or after ovulation has elapsed. This ultrasound confirms that the ovaries are at rest, i.e. that there are no cysts or a larger follicle.
- Controlled ovarian stimulation. It involves the administration of hormones to control the development of follicles. They are usually urinary or recombinant Gonadotropins. The medication should be started on the first or second day of the menstrual cycle, since the goal is to synchronize the follicles, so that they grow at the same time, until they reach the right size. This is the longest phase of ovarian stimulation and lasts 10 to 12 days.
- Follicular development and ovulation. The third phase of ovarian stimulation consists of the injection of the trigger, either hCG hormone, GnRh analogue or both. They will be responsible for stimulating the final development of the follicle and releasing the egg. This hormone is administered 32-36 hours before the follicular puncture and its objective is to achieve controlled ovulation.
In patients undergoing IVF with fresh transfer, after the follicular puncture it is necessary to prepare the endometrium for the future implantation of the embryo. If this is your case, we will instruct you to take progesterone from the same day or the day after the puncture and for several days, in order to increase the thickness of the endometrium before the embryo transfer.
Follow-up and control of ovarian stimulation phases
In each of the phases of ovarian stimulation we provide you with continuous, high quality and close medical attention to know how you are doing, how many oocytes are maturing and what is the optimal time for their extraction.
Our medical care service will advise you throughout the process and will be available 24 hours a day to answer your questions.
Many expectant mothers are also concerned about how the ovarian stimulation controls are performed, especially if you live in another city or have risk factors.
Normally, this control is done with vaginal ultrasounds and blood tests. However, nowadays we can also monitor the ovarian stimulation without the patient coming to our clinic for ultrasound controls. In fact, at Equipo Juana Crespo we have been working for a long time on the diagnosis and follow-up of fertility preservation treatments, IVF and oocyte donation through telemedicine, obtaining the same results of success as with face-to-face consultations.
How do we do it? From the clinic we provide you with the necessary equipment so that you can perform the treatment from your own home, a guided gynecological examination to be assessed by your gynecologist and your nurse remotely and in real time. Both specialists will analyze your ultrasound scans and will avoid any risk or displacement until the day of the puncture.
On the other hand, in Juana Crespo we work with a network of gynecologists around the world. If you live outside Valencia, you can consult our specialists without having to travel here until the day of the follicular puncture.
How many days does ovarian stimulation last and what medication should I take?
The ovarian stimulation treatment lasts, on average, between 10 and 12 days, although it depends on each woman.
The hormones given are the same hormones that your body produces naturally during the menstrual cycle (follicle stimulating hormone -FSH- and luteinizing hormone -LH-) to regulate the production and maturation of oocytes.
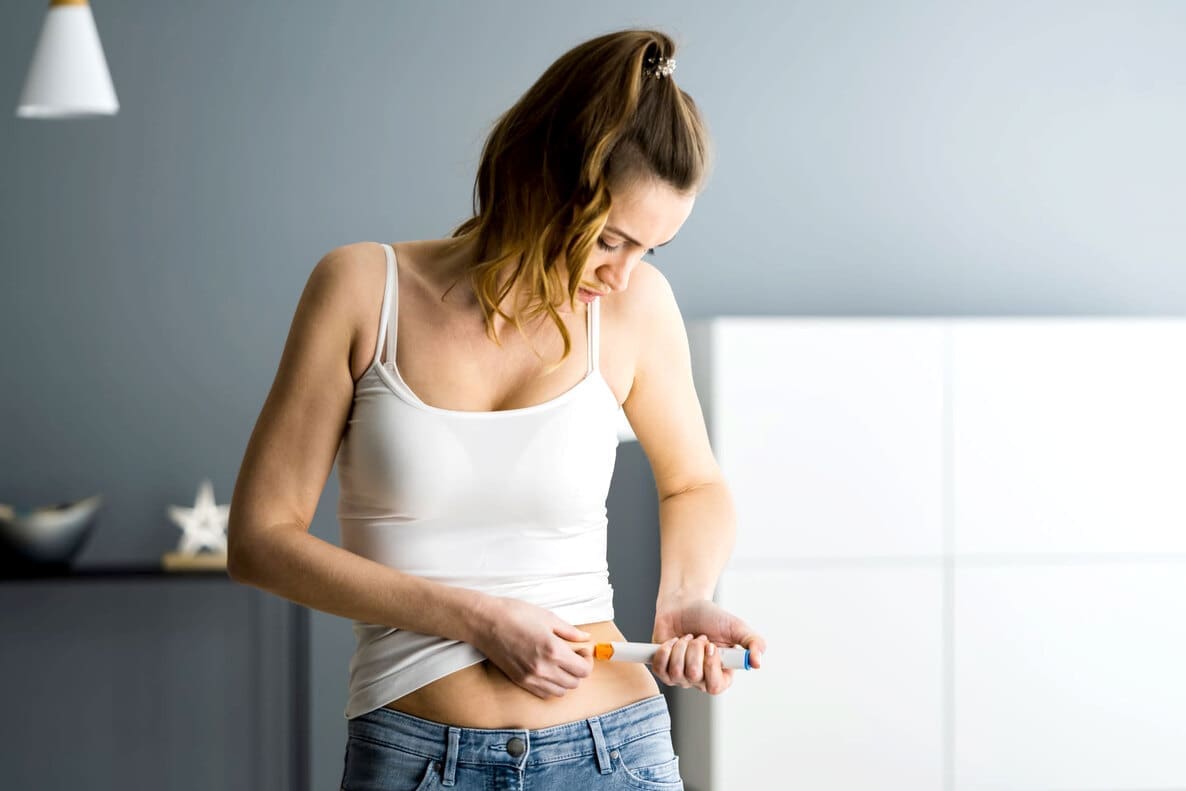
Normally, ovarian stimulation medication is administered subcutaneously, with injections that you can give yourself following our instructions.
The type of medication and its dose may vary depending on your age, the morphology of your ovaries, your hormonal analysis, your ovarian reserve, your weight or your response to previous cycles.
What guidelines or care should I follow during ovarian stimulation?
During ovarian stimulation you can follow your usual routines (go to work, practice sports, do routine leisure activities, etc.), although it is advisable to reduce nerves and stress, rest well and avoid alcohol and tobacco consumption.
Is ovarian stimulation different in older women?
Yes, as we have indicated, the hormonal treatment of ovarian stimulation is personalized and depends on various factors. One of the most important is precisely the woman’s age.
What are the side effects and what does it feel like during the process?
There is a popular belief that ovarian stimulation is fattening, that it has serious side effects or that it can bring forward menopause. However, this is not the case.
It is true that ovarian stimulation involves “altering” your hormone levels and that you may feel symptoms similar to those of menstruation.
Ovarian pain during ovarian stimulation is quite common. You may also experience mild abdominal pain and bloating, fluid retention or increased vaginal discharge.
Some women experience headaches, breast discomfort or mood swings as symptoms associated with ovarian stimulation.
Regarding the risks of medication, they are minimal, as the entire process is controlled and completely personalized.
Finally, ovarian stimulation helps to “rescue” the follicles that would have been lost in the menstrual cycle in a natural way. In this sense, hormonal treatment does not bring forward menopause nor does it pose a risk to your ovarian reserve or your future fertility.
What happens if I do not respond to ovarian stimulation?
Between 7% and 24% of patients have a low response to ovarian stimulation. This means that the eggs retrieved after follicular puncture are scarce or of poor quality.
Although the low response is confirmed once the process has been performed, some factors can help us to predict it (advanced age, reduction of ovarian mass due to surgery or endometriosis, low blood estradiol levels, etc.) and prevent it.
If the response is low, some options to achieve pregnancy are:
- Perform a pre-treatment with androgens to achieve a greater number of follicles in the following stimulation.
- To opt for a more personalized treatment with a short protocol.
- To carry out several cycles of accumulation of eggs, increasing the probability of obtaining high quality embryos.
Use donor eggs. When the low ovarian response is repeated in several cycles, the best alternative to achieve pregnancy is oocyte donation, a reproductive option with high success rates.