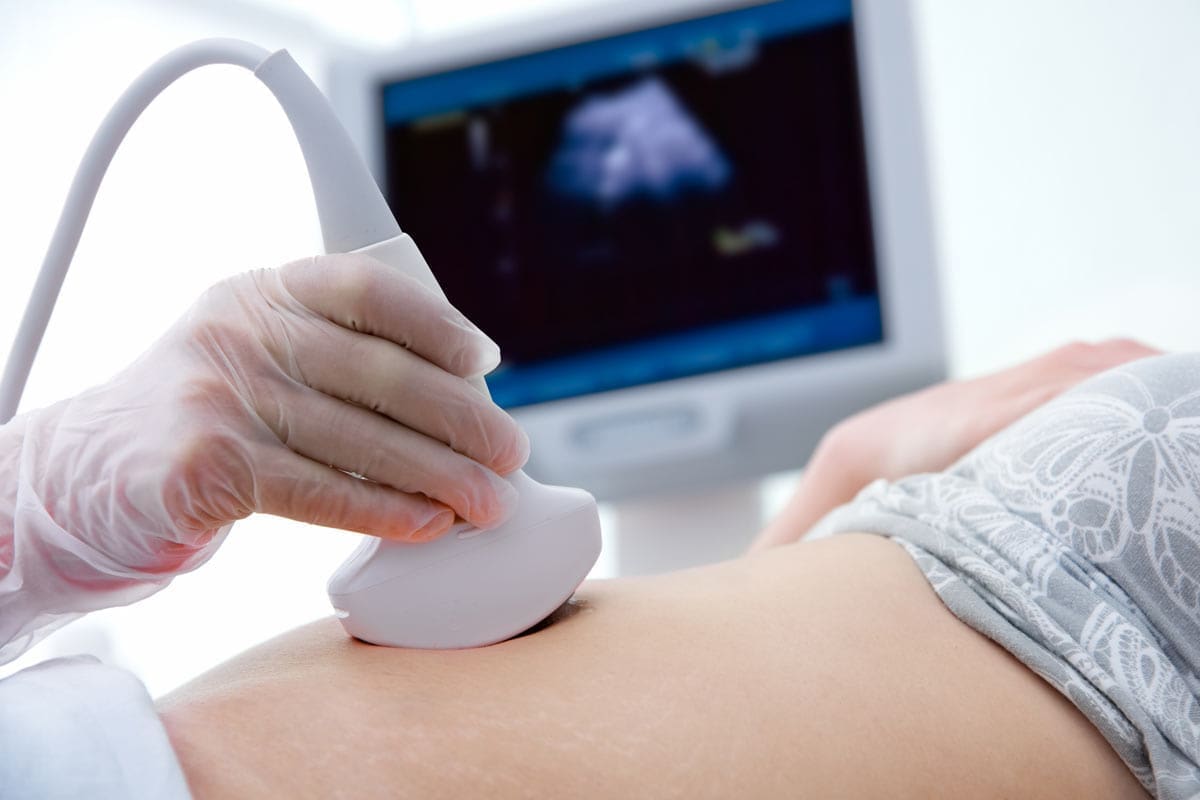
During pregnancy, women may undergo various tests to ensure that the developing baby does not suffer from genetic alterations or congenital malformations.
Non-invasive prenatal testing presents a safe, rapid, and risk-free alternative for both the mother and the baby.
To conduct this test, only a blood sample needs to be extracted from the pregnant woman, akin to a routine blood test, for analysis in the laboratory.
Why is prenatal diagnosis important?
According to the Federación Española de Enfermedades Raras (Spanish Federation of Rare Diseases), there are between 5,000 and 7,000 rare diseases, with 80% of them originating from genetics and capable of being inherited by our offspring.
It’s estimated that 3-4% of newborns will be affected by one of these conditions.
Furthermore, chromosomal abnormalities directly account for 50% of spontaneous abortions.
The term “prenatal diagnosis” encompasses a range of techniques used to detect fetal abnormalities.
Fetal abnormalities are understood as any alterations in the morphological, structural, functional, or molecular development of the fetus, both external and internal, sporadic, hereditary, unique, or multiple.
Learn about genetic compatibility testing
The techniques currently employed for prenatal diagnosis are very precise and allow the detection of congenital defects to adopt the most responsible measures during gestation and childbirth, safeguarding the health of the mother and child and improving the diagnosis of the newborn.
In summary, the advantages of prenatal diagnostic tests include:
- Early detection of fetal abnormalities.
- Early treatment of diseases in the baby.
- Enhanced control during delivery.
- Medical counseling for future parents.
Types of prenatal diagnosis
Prenatal diagnostic techniques can be either non-invasive or invasive.
Non-invasive diagnosis
These are simple tests that pose no risk to either the mother or the fetus.
In this group, we would find:
- Pregnancy monitoring ultrasounds (very useful for diagnosing fetal malformations).
- Doppler ultrasounds (important for studying anomalies in the fetal and placental circulatory system).
- Fetal DNA analysis in maternal blood (it is the most popular genetic test during pregnancy and consists of analyzing fetal DNA that circulates freely through the maternal bloodstream thanks to a blood sample).
Invasive diagnosis
They involve making a puncture or biopsy to reach the gestational sac or placenta and take a sample, which can jeopardize the pregnancy.
Within this second group, we can highlight:
- Amniocentesis (extraction of amniotic fluid through a transabdominal puncture guided by ultrasound).
- Chorionic villus sampling (obtaining a small portion of tissue from the chorionic villi of the placenta using forceps or a catheter transvaginally (through the vagina) or transabdominally (piercing through the abdomen)).
When should the non-invasive test for the detection of chromosomal abnormalities be done?
The objective of the non-invasive test is to detect and quantify specific fragments of fetal DNA present in the maternal bloodstream from the 9th week of pregnancy (from the 10th week, its sensitivity increases to 99%).
To perform this test, only a blood sample from the pregnant woman needs to be extracted and analyzed.
What type of alterations does this test detect?
Although its capacity is limited, non-invasive prenatal testing allows the detection of many genetic and chromosomal abnormalities, including:
- Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
- Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13)
- Turner syndrome (X0)
- Sex chromosome trisomies (Klinefelter syndrome (XXY), Jacobs syndrome (XYY), Triple X syndrome (XXX), or 22q deletion syndrome)
- Microdeletions (Angelman syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Cri-du-chat syndrome, or 1p36 deletion 5-17%)
- Triploidy (69 chromosomes)
Interpretation and confirmation of results
Non-invasive prenatal testing is very simple to perform, and results are obtained in a few days (on average, it takes a week).
The test result will be LOW PROBABILITY or HIGH PROBABILITY, with a test efficacy of up to 99%.
It is important to note that NIPT is a screening test, not a definitive diagnosis.
In the case of a high probability, the diagnosis must be confirmed with an invasive test that allows confirming the presence of:
- Chromosomal abnormalities.
- Hereditary genetic diseases.
- Fetal malformations.
- Infections.
In what cases is it recommended to do a genetic test during pregnancy?
Fetal DNA testing is a recommended test for all pregnant women who have completed the 10th week of gestation.
Nevertheless, it is especially important to do it in:
- Advanced maternal age women (from 38 years old).
- High-risk results in biochemical or ultrasound screening in the first trimester.
- History of pregnancies with chromosomal abnormalities.
- Naturally conceived pregnancies.
- IVF pregnancies, both with own and donated gametes.
- Twin pregnancies.
And what happens in assisted reproduction treatments with PGT?
When PGT (Preimplantation Genetic Testing) is performed to select the genetically healthiest embryos, fetal chromosomes have already been directly studied, so non-invasive prenatal testing is usually not necessary.
What is the price of non-invasive prenatal testing?
Non-invasive prenatal testing has multiple advantages compared to other prenatal tests, hence its popularity.
The most important ones are:
- Early diagnosis.
- Simplicity.
- Speed.
- Safety.
- Accuracy.
If you want to know the price of non-invasive prenatal testing, are interested, or have doubts about this prenatal diagnostic test, call us or write to us without obligation.